Why use chatbots?
Customer expectations are constantly evolving, and the tech-savvy generation is increasingly looking to resolve queries on their own. In addition, there is a continually growing expectation for round-the-clock customer service. These consumer preferences are fueling the growth of technology solutions such as chatbots. When deployed efficiently, they effectively reduce operational costs while providing 24/7 interaction with the customer. Numerous financial services institutions across the globe have differentiated their customer service by adopting chatbots and decreasing the customer service gap. A few stats that depict the importance of chatbots include:
- ~76% of consumers would trust a bot for an insurance quote
- A leading fintech company resolved more than 50% of customer inquiries without a live frontline employee
- A leading insurance company in the Netherlands helped ~85% of visitors resolve their queries through a chatbot
- A leading US bank handles more than 100 million queries via its chatbot per quarter, with ~19.5 million consumers using the chatbot
- A leading Australian bank handles ~200 banking tasks using a chatbot
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about chatbots
- What is a chatbot
- 5 types of chat capabilities
- Benefits
- Limitations
- Applications
- Platforms
- Pricing
- Chatbots and automation
- How to approach a chatbot strategy
- More automation and technology insights
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is software configured with specific instructions and responses to interact with real people and back-end systems. The set of responses is a continuously evolving library based on the inputs and queries by the user. The chatbot uses the inputs (keywords, phrases, interaction, entire text) provided by the user, compares them against the configured instructions, and uses the response library to reply to the user. It can tap into and utilize a wide range of responses – from basic text to pictures, options, map locations, links to websites, and forms.
There are mainly two types of chatbots currently available: rule-based and advanced.
Rule-based chatbots: These chatbots are deployed based on a highly structured set of instructions with standard automated responses. They have specific rules associated with certain answers and are typically used to answer very simple queries. The chatbot doesn’t evolve with time, and any upgrades must be manually configured. They are neither empathetic nor conversational and respond with basic answers or directions and links to pages. These are the most used chatbots in the market today.
Advanced chatbots: These chatbots are deployed using natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and artificial intelligence. They adapt based on consumer responses and continually evolve with time. They learn as they go and can personalize responses by understanding consumer sentiment using NLP. They can also be predictive and provide responses based on the nature of the interaction. Using these chatbots requires an extensive initial data set to train the bots before being deployed in real life. Configuration is complex and requires highly skilled personnel. Also, because of the nature of these technologies, it can be challenging to pinpoint the root cause when things go wrong.
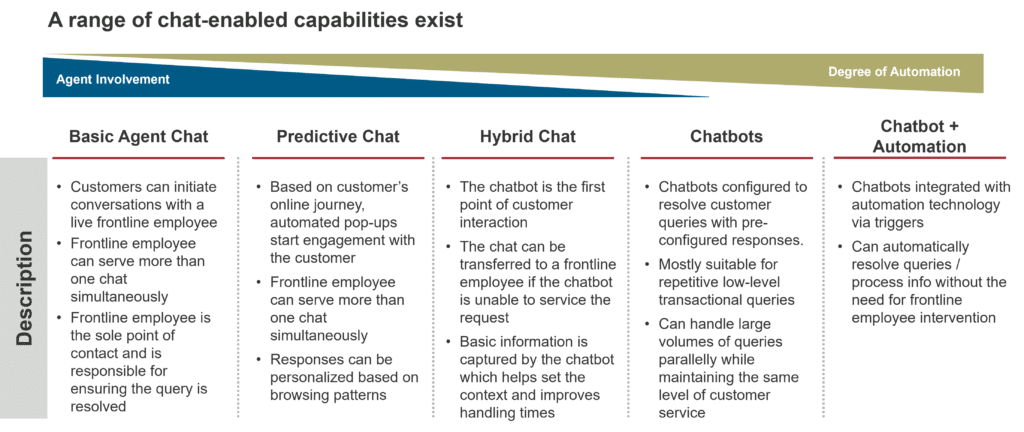
5 types of chat capabilities
Having worked in the customer service industry for decades, we have seen a range of chat capabilities. We have broken down the entire spectrum into five broad buckets that vary in the degree of automation and the amount of frontline employee involvement. Below is a description of each type of chat capability:
1. Basic agent chat
Sample functionalities include:
- Resolving most types of customer queries by frontline employees
- Basic routing based on frontline employee availability
- Use of libraries with canned responses to assist frontline employees
- History of customer interactions to improve customer service
- Call-deflection from call channel
- Embedded into a multi-channel platform (web, mobile, Facebook)
2. Predictive chat
Sample functionalities include:
- Proactively engaging customers based on browsing patterns
- Advanced routing capabilities based on customer profile and frontline employee skills
- Personalizing responses based on customer sentiment
- Real-time analytics and response triggers to assist frontline employees
3. Hybrid chat
Sample functionalities include:
- Improved customer experience as chatbots are available 24/7 to greet customers
- Improved handling time as frontline employees have basic information prior to a live chat
- Ability to resolve basic FAQ type queries and then offer to route to a frontline employee as needed
- Matched routing to direct customer requests to the most suitable frontline employees
- Load balancing based on contact center volumes
4. Chatbots
Sample functionalities include:
- Resolve low-level transactional queries (e.g., password resets, address changes, claim status)
- Integration with back-end systems to retrieve customer details and personalize service
- Direct customers to the right webpage, source of information and forms
- Ability to handle large volumes of queries parallelly
- NLP incorporation enables new questions to be answered or redirected to the right channel
5. Chatbots and automation
Sample functionalities include:
- Automatic triggers to initiate complex workflows (e.g. making policy changes, bill payment)
- Automated processing of simple or small claims from acceptance to payment, all triggered via chat
- Advanced integrations enabling chatbots to access information from legacy systems
- Advanced artificial intelligence, machine learning, and security features enable segregation of valid and fraudulent claims
Learn more about how technology and automation can accelerate your organization.
READ MOREChatbot benefits
Chatbots are increasingly used for a variety of applications. Here are some of the numerous benefits associated with chatbots:
- Instant responses: Chatbots can engage with customers without any delay or queue time, unlike frontline employees
- 24/7 availability: Unlike humans, chatbots do not have downtime and are always available to greet the customers without any compromise on quality
- Automated information collection: Chatbots can collect all the relevant information and present it to the frontline employee before engagement, providing quicker issue resolution
- Optimized service cost: Chatbots helps reduce service costs without any compromise on service delivery. Low-level transactions are dealt with by chatbots, limiting frontline employees to serve high-pressing queries.
- Ease of scalability: Chatbots can be easily upsized without the need to spend additional training hours
- Load-balancing within contact centers: Effective chatbot solutions can offload capacity from interactive voice response (IVR) and help decrease wait times leading to better customer experience
Chatbot limitations
As with any technological solution, chatbots come with their limitations.
- Lack of cognitive ability: Chatbots are programmed to answer certain types of queries, limiting any nuanced query resolution beyond the programmed rules
- Impersonal service: Standardized responses leads to a lack of personalization, which can result in a below-average customer experience
- Frequent maintenance: Truly unlocking the potential of chatbots requires regular review and optimization to meet the ever-changing demands of the customer
- Miscommunication and loss of context: Often, context is lost over messages. Customers often have to repeat themselves to a chatbot or wait to be transferred to a contact center, increasing the load.
Chatbot applications
Chatbots are most suitable for repetitive tasks that are simple and tend to involve low human cognitive application. For example, simple tasks with standard workflows that would otherwise increase call volumes in the contact center are great candidates for chatbots. Here are a few areas within financial services.
- Providing information: Tasks such as explaining standard insurance policies, hours of operations, password resets, finding the nearest branch or office, and displaying FAQs can be handled by chatbots after appropriate configurations
- Customer engagement: Chatbots have great applications to boost current business by engaging with customers to execute tasks such as providing a quote, selling products, displaying product benefits, etc.
- Execution of simple tasks: In conjunction with automation, chatbots can handle bill payments, claim status, application status, customer balances, card activation and hot listing via integrations with the back-end and core systems.
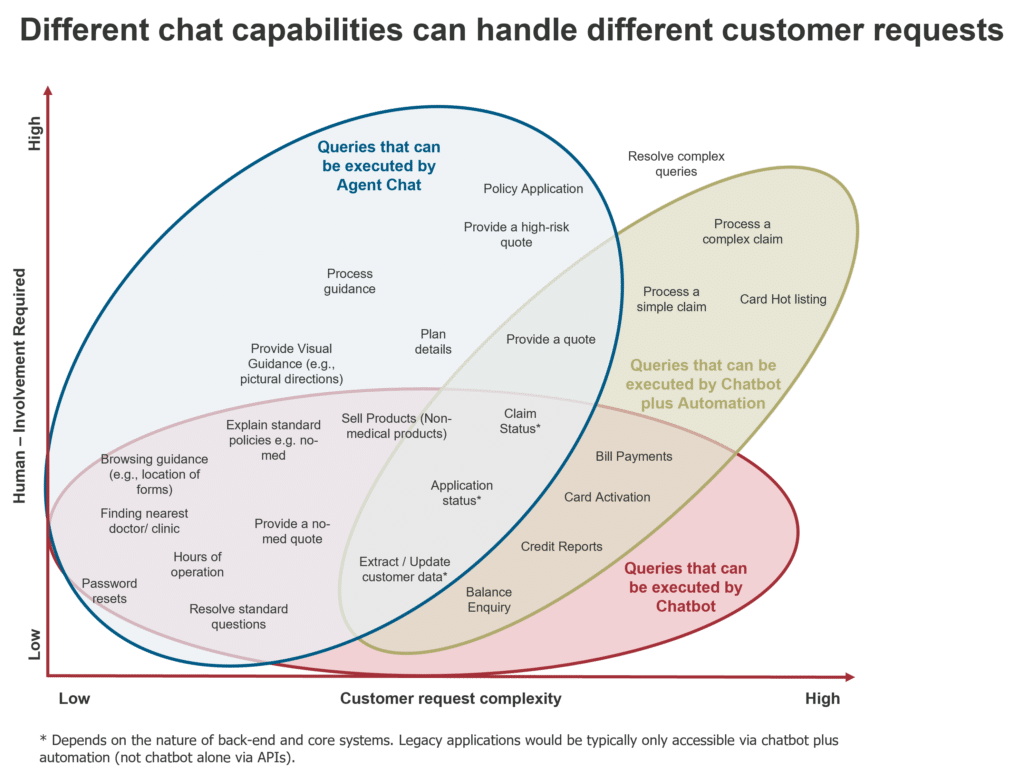
Combining different chat capabilities allows us to address customer requests through the most suitable channel while driving efficiency. Chatbots are commonly deployed as the first point of interaction for customers. Basic queries are handled in an automated method, while complex transactions are transferred to a frontline employee.
This graph represents tasks suited for chatbots compared to standard chat and automation.
Chatbot platforms
There are various companies offering chatbot solutions. They fall into three categories.
- Integrated contact center technology providers: The players have chatbots as part of their broader contact center solution offering. The chatbot integrates seamlessly with the contact center technologies from the same vendor and helps maintain a standard technology stack within the company. Most vendors offer a range of functionalities like predictive chat, intelligent routing (when implemented in combination with live chat), AI, advanced analytics, and availability across multiple channels (e.g., web, mobile, SMS, social media). Vendors in this category include Genesys, NICE inContact, Upstreamworks, Five9, Verint, Talkdesk, Oracle, Nuance
- Integrated technology solution providers: These players are predominantly technology providers with chatbots as one of their product offerings. The chatbot is integrated with relevant systems using APIs and offers functionalities like predictive chat, intelligent routing (when implemented in combination with live chat), AI, advanced analytics, availability across multiple channels (e.g., web, mobile, SMS, social media). Vendors in this bucket include Salesforce, Pegasystems, Microsoft, IBM, ai, SAP, Acquire.io
- Stand-alone providers: These are dedicated chat solution providers with a complete focus on technologies related to chat and chatbots. The solutions integrate seamlessly with leading technology vendors (e.g. contact center, back-end, and core systems) and are market leaders in the chatbot industry. The vendors offer similar functionalities as mentioned above and are at par with the previously mentioned providers. Vendors in this bucket include Liveperson, Ada, Servisbot, Amelia, Netomi
Chatbot pricing
Pricing models for chatbots depend on various factors, including the number of bots, types of features, types of integrations, number of chat sessions, types of channels (e.g. mobile, website, social media), security, the support offered and more. There are two typical pricing models:
- Subscription-based pricing: Pricing is based on the number of licenses procured and the types of features enabled within the environment. Each license has a monthly fee, and most companies that offer this model have a free trial period with limited features to test the product. For example, Genesys offers four flexible plans starting at $75 per user per month to $140 per user per month*. This pricing model is prevalent within the industry, with highly flexible options depending upon the usage of the services.
- Number of chatbots: Certain companies charge a monthly fee based on the number of chatbots deployed and the total number of chats that the chatbot is configured to handle. For example, TARS provides the option of deploying three chatbots handling 10,000 chats per month or five chatbots handling 20,000 chats per month, including two WhatsApp bots. A higher number of chatbots incentivizes the vendors to provide additional features and premium support for the customers.
*At an enterprise, most companies provide a quote after assessing the technological infrastructure in place within the company and then provide a quote based on the kind of effort that would be required to deploy a chatbot effectively.
Chatbots and automation
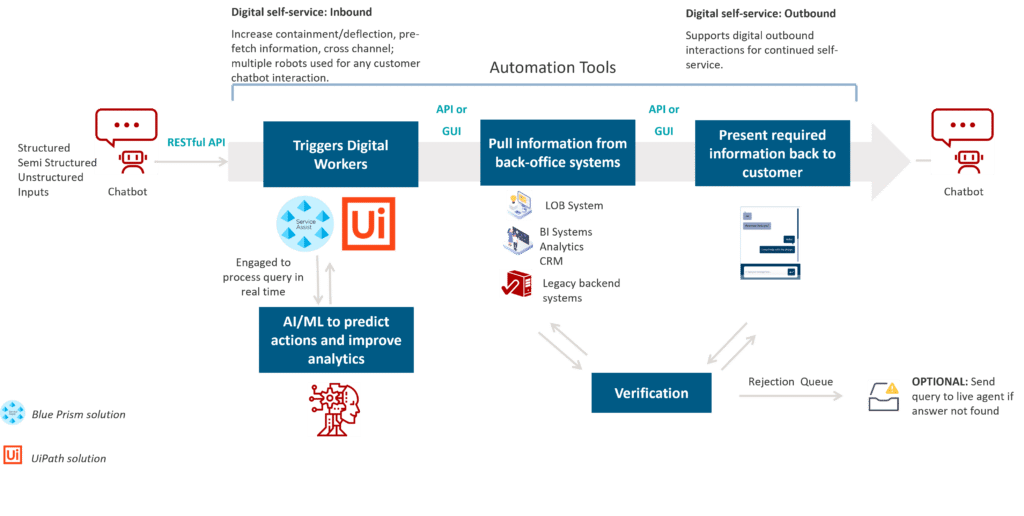
Most organizations created before the 2000s still rely on disjointed legacy systems for their core customer data and business function. Chatbots effectively bridge this gap because they can converse with customers or employees to send information, complete tasks, or capture their requests. Based on the use case, a bot can integrate with and access information from different enterprise systems (e.g. LOB core systems, CRM, business intelligence, HR knowledge bases, helpdesk, etc.) and use it as requested. Where systems have modern APIs, the chatbot can access the required information seamlessly.
The integration of chatbots and robotic process automation (RPA) and intelligent automation (IA) is a powerful combination. RPA helps chatbots effectively navigate legacy systems that do not have modern APIs. This powerful integration is a game-changer for two reasons:
- RPA powered chatbots can integrate with disparate and multiple back-end enterprise systems to retrieve information from these systems and handle more complex and real-time customer/employee requests and queries at scale.
- Chatbots can trigger RPA to perform specific mundane tasks without routing them to a frontline employee upon a user’s request.
Benefits of the integration of chatbot and RPA/IA are:
- Cost reduction by combining automation capabilities and self-service via chatbot
- Addressing higher customer expectations (e.g. 24/7 access to services)
- Increased frontline employee productivity, so frontline employees don’t have to spend time on mundane and routine activities like gathering customer data, copying information, completing paperwork, etc.
- Offering tailored customer experience by leveraging AI and machine learning to analyze large volumes of customer data and sending meaningful, contextual and individualized up-sell and cross-sell offers to customers
Example: Integration of chat and automation capabilities
How to approach a chatbot strategy
A variety of factors and inputs need to be considered before deploying an effective chatbot service within a company. Six key elements must be understood when considering chatbots:
- Customer expectations: It is critical to prioritize the list of services and tasks to be enabled by chatbots; not every service is suitable. In addition, evaluation of different chat capabilities (e.g., live chat, chatbot, chatbot plus RPA) along with alternative channels (e.g., online self-services, FAQs) will form a key input to the chatbot service offering.
- Call data and volumes: Understanding call volumes, call types, call intents and queries, and assessing the feasibility of deploying chatbot capabilities to serve some of these requests will help understand the potential efficiencies from the offering. Also, elements of call migration strategy should be considered when considering chatbots
- Web analytics & digital behaviours: Web analytics and digital user behaviour are important factors to understand customers’ interaction with digital properties. Identifying most visited pages and user interactions (e.g., how far down they scroll) informs the chatbot integration approach and lays the foundation for predictive engagement.
- Existing technology solutions and capabilities: The selection of the target chatbot technologies should be informed by the existing technology landscape. Many modern integrated solutions such as telephony (e.g. CISCO, Finesse), CRM (e.g. Salesforce), automation (e.g. Blue Prism, UiPath), and workforce management (e.g. Verint) are equipped with integrated chatbot capabilities. It is essential to select the right set of capabilities and, if needed, complement it with boutique chatbot solutions
- Core system capabilities: Existing core application landscape (e.g., modern solutions like Guidewire vs mainframe-based legacy solutions) should act as key inputs to inform the chatbot strategy (e.g., access to customer data). In many cases, a combination of chatbot and automation capabilities is advisable (e.g. when modern APIs are not available).
- People capabilities: Not every company has the right skills and capabilities to operate in the chatbot environment efficiently. Effectively utilizing chatbots requires technology affinity, highly skilled employees, and the right customer-focused approach.
These inputs inform a detailed analysis of potential opportunities, chat strategy design, alignment with the overall target operating model. This is followed up by prioritizing opportunities, identifying and selecting appropriate technologies, and a roadmap design.
Develop a chatbot strategy that works for your organization
If you are interested in chatbot strategy or assessing the fit for your company, our experienced team members have decades of relevant experience across a range of organizations, from financial services and insurance to software providers. In addition, our specialists with a focus on digital strategy and IT strategy will be happy to support you as we have supported other organizations in the past.
About the authors
Read more insights on automation and technology
Discover the potential for chatbots at your organization.
CONTACT US